HTML heading tags (<h1> to <h6>) are
structural elements used to define headings or titles within a document. By
default, browsers apply certain styles to these heading tags, and these
styles can vary slightly between browsers. Here's a general overview of the
default styles for heading tags.
-
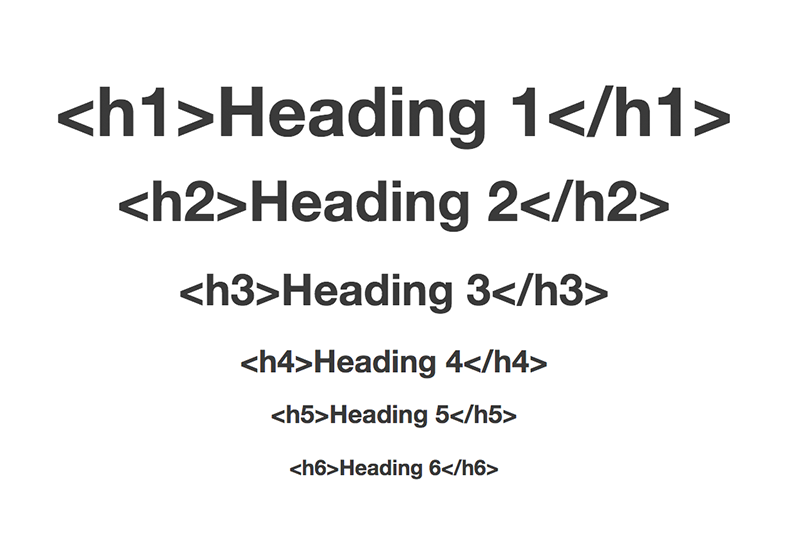
Each heading tag has a default font size, with
<h1>being the largest and<h6>the smallest. The font size decreases as the heading level increases.
h1 {
font-size: 2em; /* Typically larger */
}
h2 {
font-size: 1.5em;
}
h3 {
font-size: 1.17em;
}
h4 {
font-size: 1em;
}
h5 {
font-size: 0.83em;
}
h6 {
font-size: 0.67em; /* Typically smaller */
}
Margin and Padding:
- The default margins and padding around heading tags may vary between browsers. It's generally a good practice to reset or normalize these styles using a CSS reset or a CSS framework like Normalize.css to ensure consistent styling across different browsers.
h1, h2, h3, h4, h5, h6 {
margin-top: 0.67em; /* Adjusted for spacing between headings and other elements */
margin-bottom: 0.67em; /* Adjusted for spacing between headings and other elements */
}
Font Weight:
- Heading tags often have a bold font weight by default, emphasizing their role as headings.
h1, h2, h3, h4, h5, h6 {
font-weight: bold;
}
Line Height:
- The default line height may vary, but it is often set to provide a visually pleasing spacing between lines of text within a heading.
h1, h2, h3, h4, h5, h6 {
line-height: 1.2; /* Adjusted for good readability */
}
It's important to note that these values can be affected by user-agent stylesheets and may be overridden by custom styles in your CSS. To ensure consistent styling and improve cross-browser compatibility, web developers often use a CSS reset or normalization techniques at the beginning of their stylesheets. This helps create a consistent baseline for styling across different browsers and devices.




0 Comments